
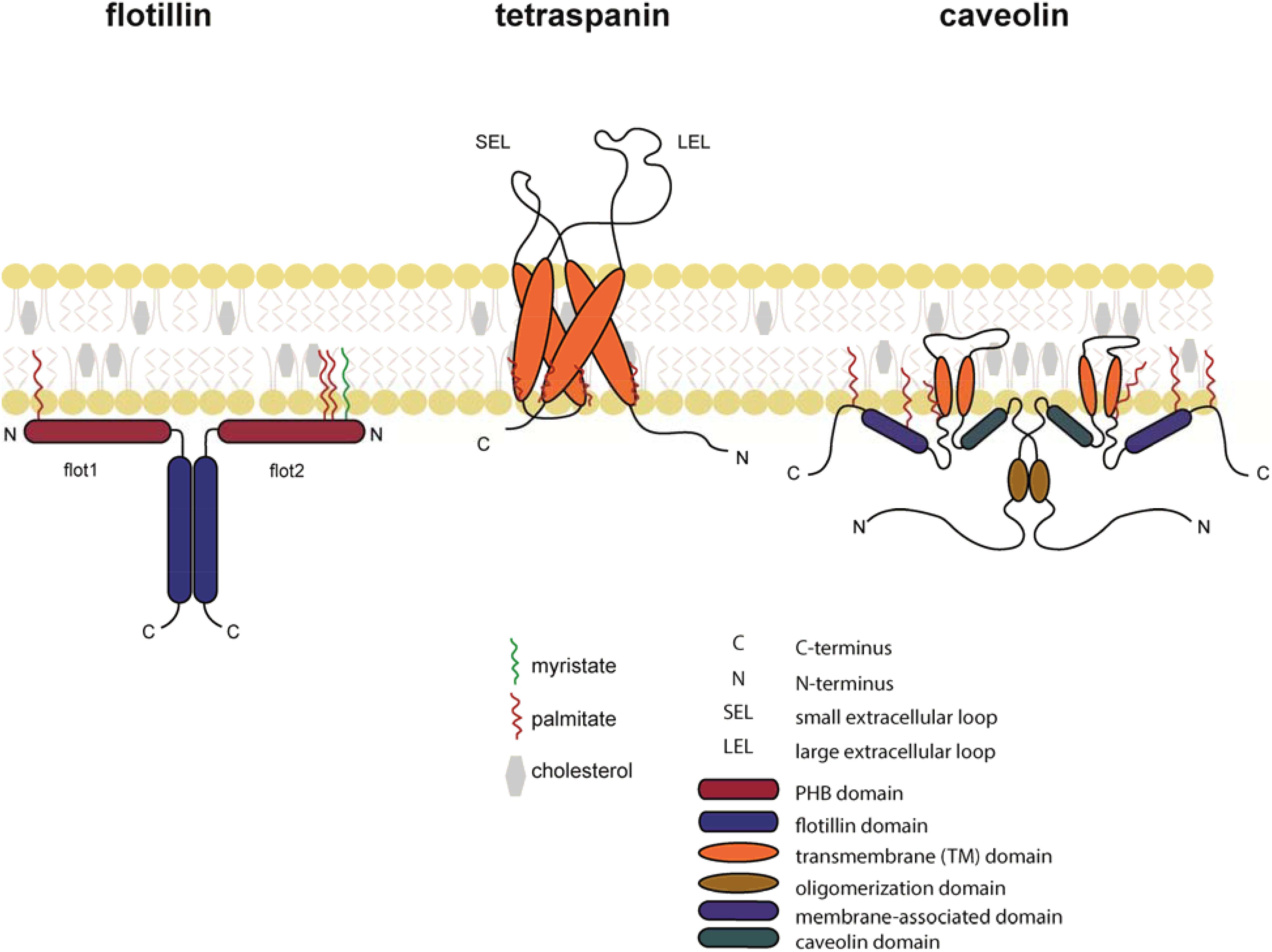
D1-D2 and D3 were further shown to compete with TGF-β(TβRII)2 and TGF-β for binding to TβRI and TβRII, respectively. We demonstrate that binding is modular, with D1-D2 binding to TβRI and D3 binding to TβRII. Here, we used surface plasmon resonance, isothermal calorimetry, NMR spectroscopy, and mutagenesis to investigate how TGM binds the TGF-β receptors. However, the molecular determinants of binding are unclear. Though lacking homology to TGF-β, TGM binds directly to the TGF-β receptors TβRI and TβRII and stimulates the differentiation of naïve T-cells into Tregs. TGM comprises five complement control protein (CCP)-like domains, designated D1-D5. N2 - The mouse intestinal helminth Heligmosomoides polygyrus modulates host immune responses by secreting a transforming growth factor (TGF)-β mimic (TGM), to expand the population of Foxp3+ Tregs. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. Molecular graphics and analyses were performed with UCSF Chimera, which is developed by the Resource for Biocomputing, Visualization, and Informatics at the University of California, San Francisco supported by NIGMS P41-GM103311. H.), the Wellcome Trust through an Investigator Award to RMM ( Ref 219530 ), and the Wellcome Trust core-funded Wellcome Centre for Integrative Parasitology ( Ref: 104111 ). This research was supported by the NIH ( GM58670 and AI53915 awarded to A. H.), the Wellcome Trust through an Investigator Award to RMM (Ref 219530), and the Wellcome Trust core-funded Wellcome Centre for Integrative Parasitology (Ref: 104111). This research was supported by the NIH (GM58670 and AI53915 awarded to A. The authors would like to thank Mike Delk for assistance with the NMR instrumentation and Henry McSorley and Matthew Whitley for providing valuable comments on the manuscript. T1 - Convergent evolution of a parasite-encoded complement control protein-scaffold to mimic binding of mammalian TGF-β to its receptors, TβRI and TβRII Though lacking homology to TGF-β, TGM binds directly to the TGF-β receptors TβRI and TβRII and stimulates the differentiation of na 2022 The Authors", polygyrus, suggest that TGM is part of a larger family of evolutionarily plastic parasite effector molecules that mediate novel interactions with their host.Ībstract = "The mouse intestinal helminth Heligmosomoides polygyrus modulates host immune responses by secreting a transforming growth factor (TGF)-β mimic (TGM), to expand the population of Foxp3+ Tregs. These results, together with the identification of other secreted CCP-like proteins with immunomodulatory activity in H. Through NMR shift perturbations and binding studies of TGM-D3 and TβRII variants, TGM-D3 was shown to occupy the same site of TβRII as bound by TGF-β using both a novel interaction surface and the hypervariable loop. TGM-D3 also incorporates a long structurally ordered hypervariable loop, adding further potential interaction sites. The solution structure of TGM-D3 revealed that TGM adopts a CCP-like fold but is also modified to allow the C-terminal strand to diverge, leading to an expansion of the domain and opening potential interaction surfaces. D1-D2 and D3 were further shown to compete with TGF-β(TβRII) 2 and TGF-β for binding to TβRI and TβRII, respectively.
Though lacking homology to TGF-β, TGM binds directly to the TGF-β receptors TβRI and TβRII and stimulates the differentiation of naïve T-cells into T regs. The mouse intestinal helminth Heligmosomoides polygyrus modulates host immune responses by secreting a transforming growth factor (TGF)-β mimic (TGM), to expand the population of Foxp3 + T regs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
